Hope and Healing: Type 2 Diabetes Remission with Lifestyle Medicine
By Jean Tips, Sr. Director of Communications and Public Affairs

To call type 2 diabetes a pandemic may sound overly dramatic. But given its global prevalence and growth in incidence, “epidemic” may fall short in describing the scale of the problem. Once a disease affects large populations across borders, it can be regarded as a pandemic. It is one of the fastest growing health conditions inside and outside the U.S. This burgeoning chronic disease creates human suffering among both adults and children, lowered workforce productivity, clinician burnout, and financial unsustainability for families and the nation as a whole. Something must be done about this preventable, treatable, and reversible problem.
This article delves into the critical issue of type 2 diabetes, its staggering economic costs, genetic predisposition, racial disparities, and dire complications, such as amputations. It explores how lifestyle medicine offers a beacon of hope and healing for both patients and clinicians.
Table of Contents
Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults
Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Childhood
Financial Costs of Diabetes
Genetic Predisposition
Diabetes Disparities
Complications from Diabetes
There is a Solution
ACLM’s Position Statement
Expert Consensus Statement
Clinical Resources
Clinical Education
Patient Advocacy–Informed Consent
Conclusion
Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults
From 2001 to 2020, diabetes prevalence significantly increased among U.S. adults 18 or older. As of the latest data reported by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC):
- 37.3 million people (about 1 in 10) have diabetes, approximately 90-95% of whom have type 2 diabetes—that’s 11.3% of the U.S. population.
- 28.7 million people have been diagnosed with diabetes.
- 8.5 million people who have diabetes have not been diagnosed and do not know they have it.
- 96 million people aged 18 years or older have prediabetes (38.0% of the adult U.S. population)
- 65 years or older: 26.4 million people aged 65 years or older (48.8%) have prediabetes
- Diabetes is the eighth leading cause of death in the United States (and may be underreported).
Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Childhood
Historically, type 2 diabetes usually developed later in life, and hence used to be termed “adult-onset diabetes.” However, in recent decades, type 2 diabetes has increased among U.S. children and adolescents aged 10 to 19. Rates differ by racial and ethnic group.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) reports that researchers forecast a growing number of people under age 20 newly diagnosed with diabetes during 2017–2060. This expected upward trend may lead to as many as 220,000 young people having type 2 diabetes in 2060 —a nearly 700% increase.
Financial Costs of Diabetes
The financial costs of diagnosed diabetes are astronomical. Growth in the absolute number of people with diabetes contributes to increased health care expenditures, particularly per capita spending on inpatient hospital stays and prescription medications.
The enormous economic toll of diabetes burdens society through direct medical and indirect costs. According to a new report from the ADA:
- The total estimated cost of diagnosed diabetes in the U.S. in 2022 was $412.9 billion, including $306.6 billion in direct medical costs and $106.3 billion in indirect costs attributable to diabetes.
- For cost categories analyzed, care for people diagnosed with diabetes accounts for 1 in 4 health care dollars in the U.S., 61% of which are attributable to diabetes.
- On average people with diabetes incur annual medical expenditures of $19,736, of which approximately $12,022 is attributable to diabetes.
- People diagnosed with diabetes, on average, have medical expenditures 2.6 times higher than what would be expected without diabetes.
- Glucose-lowering medications and diabetes supplies account for ∼17% of the total direct medical costs attributable to diabetes.
- Major contributors to indirect costs are reduced employment due to disability ($28.3 billion), presenteeism ($35.8 billion), and lost productivity due to 338,526 premature deaths ($32.4 billion).
Genetic Predisposition
Type 2 diabetes is said to have a stronger link to family history and lineage than type 1, and studies of twins have shown that genetics play a very strong role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Race can also play a role.
Yet, it also depends on environmental factors and lifestyle influences. Obesity tends to run in families, and families often have similar eating and exercise habits.
The lifetime risk of developing Type 2 diabetes if a parent has it is 40%. If both parents have it, the risk jumps to 70%.
Diabetes Disparities
Certain racial and ethnic groups are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, with American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, and Hispanic populations having higher prevalence rates.
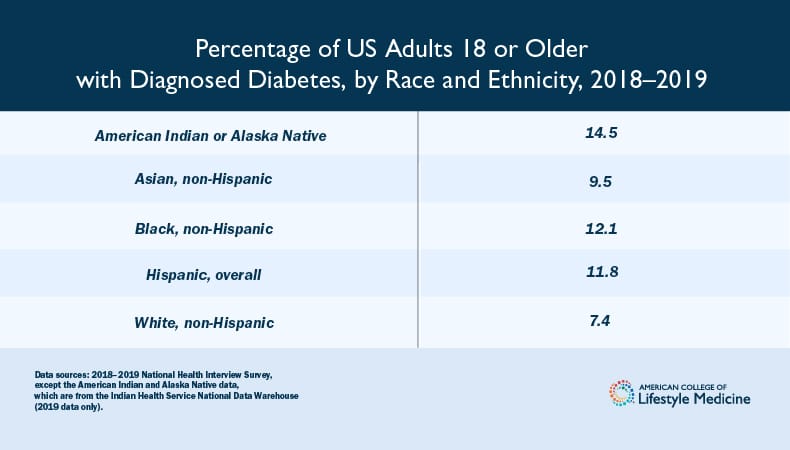
Complications from Diabetes
A toe, foot or leg is cut off by a doctor about 150,000 times a year in America, making the United States a world leader of these amputations according to the National Institutes of Health. The CDC reports lower-limb amputations are increasing in the US, and 80% are a result of complications from diabetes. From 2009 to 2019, the number of diabetes-related hospitalizations due to amputation doubled.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), about 130,000 people in the United States who have diabetes have amputations each year. The ADA says lower-extremity amputations are 10 times more common in people with diabetes than in persons who do not have diabetes.
Time Magazine has reported that Blacks who live in Southern States with diabetes are the most apt to receive amputations.

There is a Solution
Type 2 Diabetes Is Preventable, Treatable and In Some Cases Reversible
A diagnosis of type 2 diabetes doesn’t have to be permanent, sentencing patients to a lifetime of medication, procedures, devastating complications, and hospitalizations. And for clinicians, there is hope and healing provided by a growing specialty area that treats the root cause of T2D, not merely managing symptoms but offering health restoration.
That specialty is lifestyle medicine.
In lifestyle medicine, the clinical goal is health with no evidence of disease. Remission is the return to a state of non-disease as determined by the failure to meet the recognized criteria for diagnosing the disease. Remission does not necessarily equate to a state of no evidence of disease. For example, a return to glucose levels in the range of “prediabetes” are consistent with various definitions of remission of type 2 diabetes but are not adequate to meet criteria for no evidence of disease.
Reversal is the process of disease treatment with the clinical goal of health with no evidence of the disease. LM intensivists are best poised to support patients in achieving optimal health and remission of disease, by engaging in reversal in the context of ITLC treatment.

ACLM’s Position Regarding Type 2 Diabetes
“The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) published a position statement in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine in June of 2020, “Type 2 Diabetes Remission and Lifestyle Medicine – A Position Statement from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine” that concludes:
“Sufficiently intensive lifestyle intervention (intensive therapeutic lifestyle change), particularly adopting a predominantly whole food, plant-based dietary pattern, exercise, and sleep, may be comparable to bariatric surgery, a commonly recognized means of effectively achieving T2D remission, but without the potential for side effects.”
Furthermore, studies have shown that the approach advocated by lifestyle medicine physicians can often and reduce or eliminate the need for prescription medications, including insulin.
T2D Assets from ACLM
ACLM aims to help eradicate this scourge through a broad array of assets:
Expert Consensus Statement
To assist clinicians in achieving remission of type 2 diabetes in adults using diet as a primary intervention, ACLM published an expert consensus statement in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine in May 2022, “Dietary Interventions to Treat Type 2 Diabetes in Adults with a Goal of Remission.”
The statement was endorsed by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE), supported by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND) and co-sponsored by the Endocrine Society.
Expert consensus was achieved for 69 statements pertaining to diet and remission of T2D, dietary specifics and types of diets, adjuvant and alternative interventions, support, monitoring, adherence to therapy, weight loss, and payment and policy.
Clinicians can use these statements to improve quality of care, inform policy and protocols, and identify areas of uncertainty.
Clinical Resources
Research
The following research highlights key findings supporting the efficacy of lifestyle medicine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. (To read more about current projects and other research in support of the advancement of knowledge in the field of lifestyle medicine visit Lifestyle Medicine Research.)
“Remission of Type 2 Diabetes After Treatment With a High-Fiber, Low-Fat, Plant-Predominant Diet Intervention: A Case Series,” published in the June 2023 American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, outlines how a lifestyle-based treatment intervention promoting adherence to a plant-predominant diet and integrated as part of routine care can successfully achieve T2D remission in wellness clinic patients.
The series demonstrates that achieving type 2 diabetes remission is possible through a healthy diet without severe calorie restriction or liquid meal replacements. In the study, 59 patients with type 2 diabetes enrolled in a cardiac wellness program and experienced significant improvements in blood glucose control, and some even achieved full remission, by following a low-fat, whole food, plant-based diet. This highlights the significance of offering all patients the chance to make lifestyle changes as part of their routine care for treating type 2 diabetes.
“Medication Deprescribing Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Qualitative Case Series of Lifestyle Medicine Practitioner Protocols,” published in Clinical Diabetes in August 2022, provides protocols for medication deprescribing in type 2 diabetes patients following successful lifestyle medicine interventions. The study addresses the need for safe and effective deprescribing guidelines, as intensive lifestyle changes can lead to decreased blood sugar levels, potentially causing hypoglycemia if medication adjustments are not made. These protocols will be valuable resources for clinicians to reduce the reliance on prescription medications and support patients in achieving remission through evidence-based lifestyle medicine practices.
A meta-epidemiological study, “Commonalities among dietary recommendations from 2010-2021 clinical practice guidelines: A meta-epidemiological study from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine,” published in Advances in Nutrition in May 2023, synthesizes recommendations from 78 clinical practice guidelines for major chronic conditions and general health promotion. This study concluded:
“…These findings support both ACLM’s dietary position statement and its recent expert consensus statement that the most effective dietary intervention for achieving T2D remission is whole, plant-based foods with minimal consumption of meat and other animal products…”
Clinical Education
Created by the foremost experts in lifestyle medicine and food as medicine, ACLM’s array of diabetes and food as medicine CME/CE courses address the need for quality, evidence-based nutrition education, missing in medical education.
These include:
- “Remission of Type 2 Diabetes and Reversal of Insulin Resistance Certificate Course.” This 18-hour CME/CE/MOC certificate course equips clinicians to use intensive, evidence-based lifestyle medicine therapies to send type 2 diabetes into remission and reverse insulin resistance. Created by experts and researchers who have had proven success in treating patients with diabetes using lifestyle medicine, upon completion you will earn a certificate and be immediately prepared to address diabetes and insulin resistance in powerful new ways.
Patient Advocacy
Informed Consent
In 2020 ACLM introduced a Type 2 Diabetes Bill of Rights aimed at empowering patients and raising awareness about their rights to evidence-based lifestyle medicine therapeutic approaches as a primary treatment option. ACLM believes that it is crucial to offer this treatment option at the time of diagnosis to ensure fully informed consent.
Conclusion
Using lifestyle medicine, clinicians can learn how to treat and, in some cases, reverse type 2 diabetes. ACLM can be your resource for restoring health to those with an existing diagnosis of this disease and preventing those with prediabetes from progressing to full diagnosis. It is not the life sentence that some may think.
More From ACLM in Support of The Use of Lifestyle Medicine to Tackle Type 2 Diabetes
Read
Addressing Diabetes Among Hispanic Americans
Whole Food, Plant-Based Diet’s Impact on Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes: A Breakthrough Study
Type 2 Diabetes Remission is Possible Without Severe Calorie Restriction
Medication Deprescribing Protocols for Type 2 Diabetes
The Benefits of Plant-Based Nutrition: Treatment and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
How One Physician Rediscovered Her Passion Through Lifestyle Medicine
“Your results are normal!” The story of how one woman with diabetes and chronic fatigue restored her health









